Strategies for School Leaders and Educators
A picture of a neon sign that says “You belong here.”
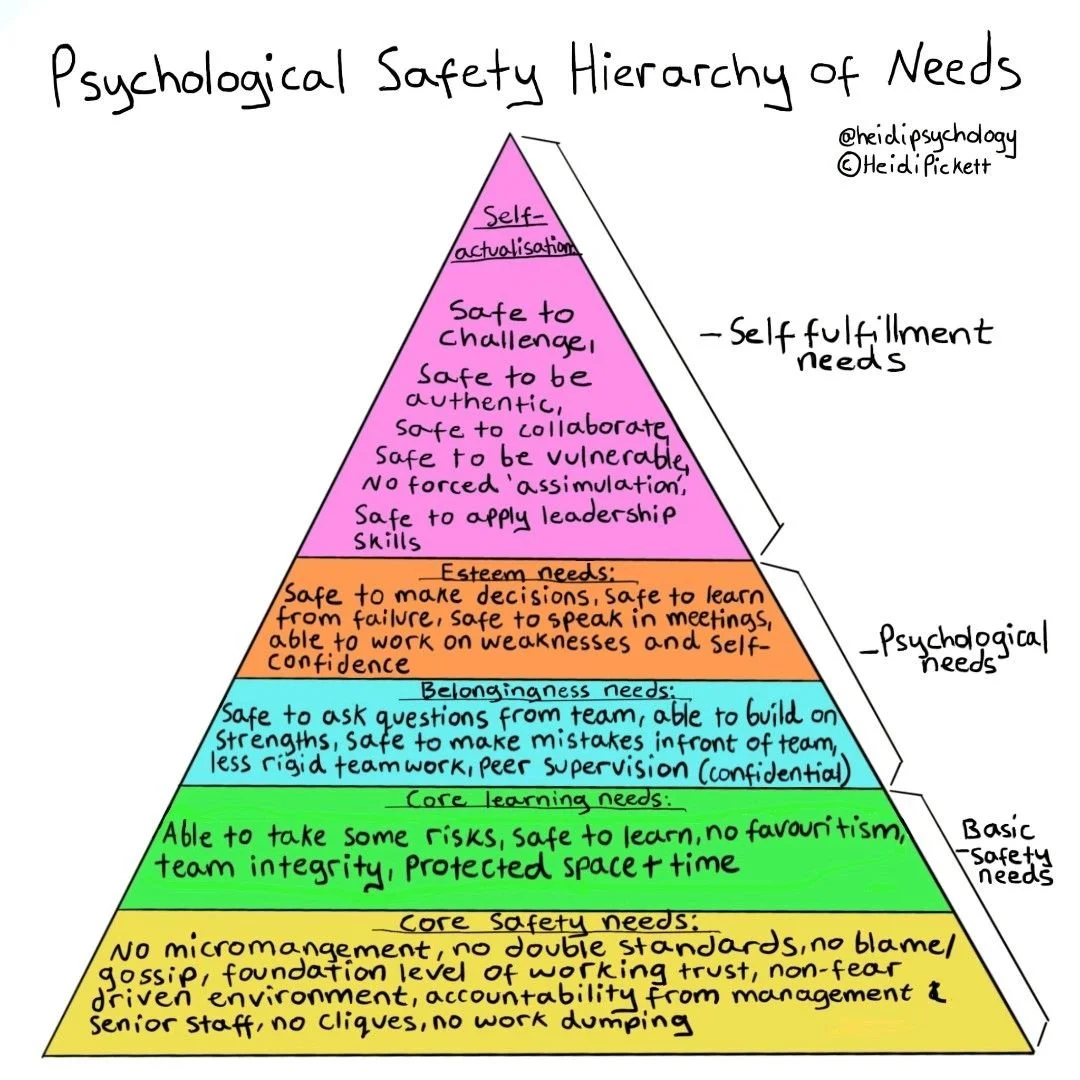
Fostering Psychological Safety in Schools: Strategies for a Supportive Learning Environment
Psychological safety in schools is essential for both students and staff to feel supported, valued, and comfortable taking risks. It forms the foundation of an inclusive learning environment where individuals can express ideas, ask questions, and participate fully without fear of embarrassment or judgment. Research consistently shows that psychological safety enhances collaboration, deepens learning, and improves student outcomes (Edmondson, 1999; Senge et al., 2000).
Why Psychological Safety Matters in Education
A psychologically safe school environment fosters:
✅ Open communication and curiosity
✅ Willingness to take academic risks
✅ Higher student engagement and participation
✅ Stronger relationships between students, teachers, and administrators
Below are 10 key strategies to create a psychologically safe school environment.
1. Model Vulnerability and Openness
🔹 Why it matters: When school leaders and educators model vulnerability—admitting mistakes and demonstrating a growth mindset—it sends a message that learning is a continuous journey.
🔹 How to implement:
Share personal stories of challenges and growth.
Normalize making mistakes and discussing lessons learned.
Create an environment where admitting uncertainty is encouraged.
🔹 Research-backed insight: Amy Edmondson’s research emphasizes that leaders who model vulnerability foster a safe space for risk-taking (Edmondson, 1999).
2. Encourage Questions and Curiosity
🔹 Why it matters: Students who feel comfortable asking questions develop deeper critical thinking skills and confidence in learning.
🔹 How to implement:
Use open-ended questions to spark discussion.
Praise students for their curiosity.
Ensure every question is treated with value, reinforcing a growth mindset.
🔹 Research-backed insight: Carol Dweck’s work on growth mindset suggests that encouraging questions fosters intelligence and resilience (Dweck, 2006).
3. Establish Clear Expectations for Respectful Communication
🔹 Why it matters: When students know that respectful interactions are expected and enforced, they feel safer expressing their ideas.
🔹 How to implement:
Set and reinforce classroom norms for discussions.
Teach active listening and constructive feedback.
Promote empathy in student interactions.
🔹 Research-backed insight: Clear communication norms increase participation and psychological safety in schools (Korthagen, 2004).
4. Celebrate Mistakes as Learning Opportunities
🔹 Why it matters: Students should see mistakes as stepping stones to success rather than failures.
🔹 How to implement:
Reframe mistakes as learning opportunities.
Guide students through reflection on what went wrong and how to improve.
Celebrate resilience and perseverance.
🔹 Research-backed insight: Jo Boaler’s research shows that embracing mistakes leads to deeper understanding and critical thinking (Boaler, 2016).
5. Build Trust Through Relationships
🔹 Why it matters: Strong relationships create a sense of belonging and emotional security in learning spaces.
🔹 How to implement:
Take time to understand students’ backgrounds and interests.
Use one-on-one check-ins to offer personalized support.
Foster connections through team-building activities.
🔹 Research-backed insight: Trust between educators and students leads to greater engagement and better academic outcomes (Bryk & Schneider, 2002).
6. Provide Autonomy and Choice in Learning
🔹 Why it matters: Students who have autonomy feel more in control of their learning, increasing motivation and confidence.
🔹 How to implement:
Allow students to choose from different assignment formats.
Offer flexible learning paths based on interests.
Give students a say in classroom decisions.
🔹 Research-backed insight: Deci & Ryan’s self-determination theory highlights the importance of autonomy in fostering motivation and safety (Deci & Ryan, 2000).
7. Encourage Collaboration Over Competition
🔹 Why it matters: Competitive environments can create fear of failure, while collaboration fosters peer support.
🔹 How to implement:
Use group projects and peer learning activities.
Reinforce collective success over individual competition.
Build a classroom culture that values teamwork.
🔹 Research-backed insight: Collaborative learning enhances mutual trust and psychological safety, leading to better academic performance (Johnson & Johnson, 2009).
8. Provide Immediate, Constructive Feedback
🔹 Why it matters: Timely and supportive feedback encourages students to take academic risks without fear of harsh criticism.
🔹 How to implement:
Give specific praise alongside improvement suggestions.
Avoid overly critical feedback that discourages effort.
Frame feedback as part of the learning process rather than evaluation.
🔹 Research-backed insight: Effective feedback increases student engagement and fosters resilience (Hattie & Timperley, 2007).
9. Develop Inclusive Practices
🔹 Why it matters: When students see diverse perspectives represented in their learning, they feel valued and respected.
🔹 How to implement:
Incorporate diverse stories, authors, and cultures in the curriculum.
Address bias and equity issues in the classroom.
Celebrate different learning styles and backgrounds.
🔹 Research-backed insight: Inclusive education enhances student engagement and belonging, which are crucial for psychological safety (Banks, 2009).
10. Provide Emotional and Social Support
🔹 Why it matters: Emotional safety is key to academic success and overall well-being.
🔹 How to implement:
Integrate Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) into the curriculum.
Teach skills like emotional regulation, empathy, and conflict resolution.
Offer mental health resources and counseling support.
🔹 Research-backed insight: Schools that implement SEL programs see higher academic achievement and improved classroom environments (CASEL, 2015).
Creating a Culture of Psychological Safety in Schools
Fostering psychological safety in schools isn’t just about avoiding harm—it’s about actively building an environment where students and staff feel safe to explore, grow, and succeed. By implementing these strategies, educators and school leaders can create classrooms that encourage risk-taking, promote collaboration, and nurture an inclusive space where everyone thrives.
Key Takeaways:
✔ Psychological safety leads to better learning outcomes and student well-being.
✔ Trust, respect, and openness are foundational elements.
✔ Educators play a crucial role in shaping a supportive environment.
By embracing these principles, we can transform schools into spaces where both students and staff feel seen, heard, and empowered to reach their full potential.
Ready to Build a Safer Learning Environment?
Start by integrating one or more of these strategies today. Small changes can create big impacts in fostering psychological safety in schools!
👉 What’s one strategy you’ll implement in your classroom or school? Let’s discuss in the comments!